BAKING POWDER – LEAVENING AGENT
$2.51 – $5.16
Baking powder is comprised of baking soda and a dry acid, like cream of tartar or sodium aluminum sulfate. Since the acid in baking powder is dry, the baking soda does not react until combined with a liquid. Baking powder is a mixture of sodium bicarbonate, other bicarbonates, and acid salts. Unlike baking soda, baking powder is a complete leavening agent, meaning it contains both the base (sodium bicarbonate) and acid needed for the product to rise.
Difference Between Baking Soda and Baking Powder?
The primary difference between baking soda and baking powder is that baking powder already contains an acid in the chemical mixture, whereas baking soda needs an acidic ingredient to create the rising reaction. Use baking soda in recipes that have acidic ingredients like buttermilk, lemon juice, or vinegar; use baking powder in recipes that do not have acidic ingredients, like biscuits, corn bread, or pancakes.
The key differences between baking soda and baking powder are tabulated below:
| Baking Soda | Baking Powder |
| Has only one ingredient – Sodium Bicarbonate | Consists of many ingredients including Bicarbonates (typically baking soda), and acid salts. |
| Does not contain Monocalcium Phosphate | Contain Monocalcium Phosphate, which reacts with NaHCO3 when wetted and heated. |
| Reacts immediately with acids | It does not immediately react when exposed to acids. |
| Short leavening process | The leavening process extended with the help of a second acid. |
| Baking products formed when baking soda is used are not as fluffy when compared to baking powder products, due to shorter reaction duration. | Gives fluffier products from baking |
Can You Substitute Baking Powder for Baking Soda?
If you don’t have baking soda on hand, you can substitute with baking powder—just use three times as much baking powder as baking soda in the recipe. For example, if a recipe calls for one teaspoon of baking soda, use three teaspoons of baking powder.
However, this substitute can backfire in one of the following ways:
- The final product is too acidic and bitter. This would be a result of too much baking powder.
- The final product is dense and hard. This would be a result of not enough baking powder.
- The final product is too salty. Baking powder contains more sodium than baking soda (so watch for the additional salt in the recipe!).
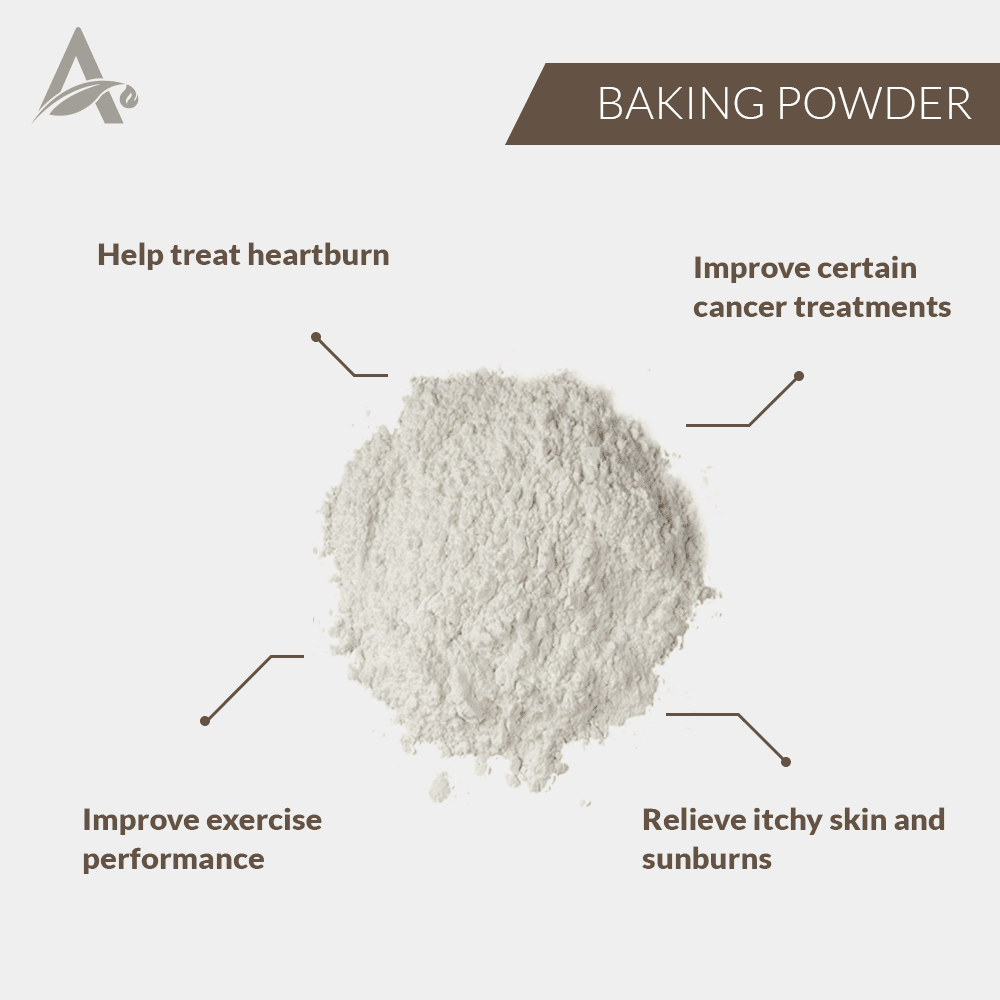
Benefits:
Helps us in preventing and curing the following:
Other Names:
Baking powder, Leavening Agent
Safety Information:
- For Natural Taste & Freshness, Keep it in cool and dry place.
- Avoid direct Sunlight & Do not Refrigerate.
- Store the contents in an Airtight Container after opening the package.
- All herbal medicine should be used under Medical Supervision only.


OOPS!!
You total cart weight has exceeded 1800 grams. Reduce it to max permissible value for COD fulfillment.


Important!!
We value your decision and will ship your product. Would you like to re-consider on paying ₹___ extra over & above product cost. You can save the same by opting a pre-payment.
Pre-Payment Continue with COD| Net Weight | 100 gm, 250 gm, 400 gm, 900 gm |
|---|
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Related products
Himalaya Herbs
Spices



























































































Reviews
There are no reviews yet.